Did you know that spinal cord and brain injuries are the most common cause of paraplegia, with spinal cord injuries affecting more than seventeen thousand people annually in America and brain injuries affecting up to 1.5 million per year? [1] A 2013 study done by Christopher & Dana Reeve Foundation revealed that about 1 in 50 people live with paralysis, nearly 5.4 million people. This is equal to the combined populations of Philadelphia, Los Angeles, and Washington, D.C. [2]
Despite the high number of people who need assistive devices like wheelchairs and walkers to move about and complete daily activities, little has been done to advance innovation in that field. That is, until the last decade when robotic legs (medical exoskeletons) were introduced in rehabilitation and recovery centers. Now, patients with paraplegia aren’t limited to a wheelchair, which may have access and mobility issues. This new innovation has led to the development of external robotic devices which can help enhance recovery through repetitive movement and improved neural plasticity. Additionally, they can serve as mobility support beyond walkers, wheelchairs, and orthoses. [3]
According to the Exoskeleton Industry 2019 Global Market research report [4], the increased uptake of exoskeletons in the medical industry has encouraged companies to invest more in research and development.
Are robotic legs the answer to helping people with spinal cord injuries, neurological disorders, and strokes regain independent function and their ability to walk again? In this article, we will break down what robotic legs are, the paraplegic conditions that are supported by robotic legs, the benefits of robotic legs, and where you can get them.
What Are Robotic Legs?

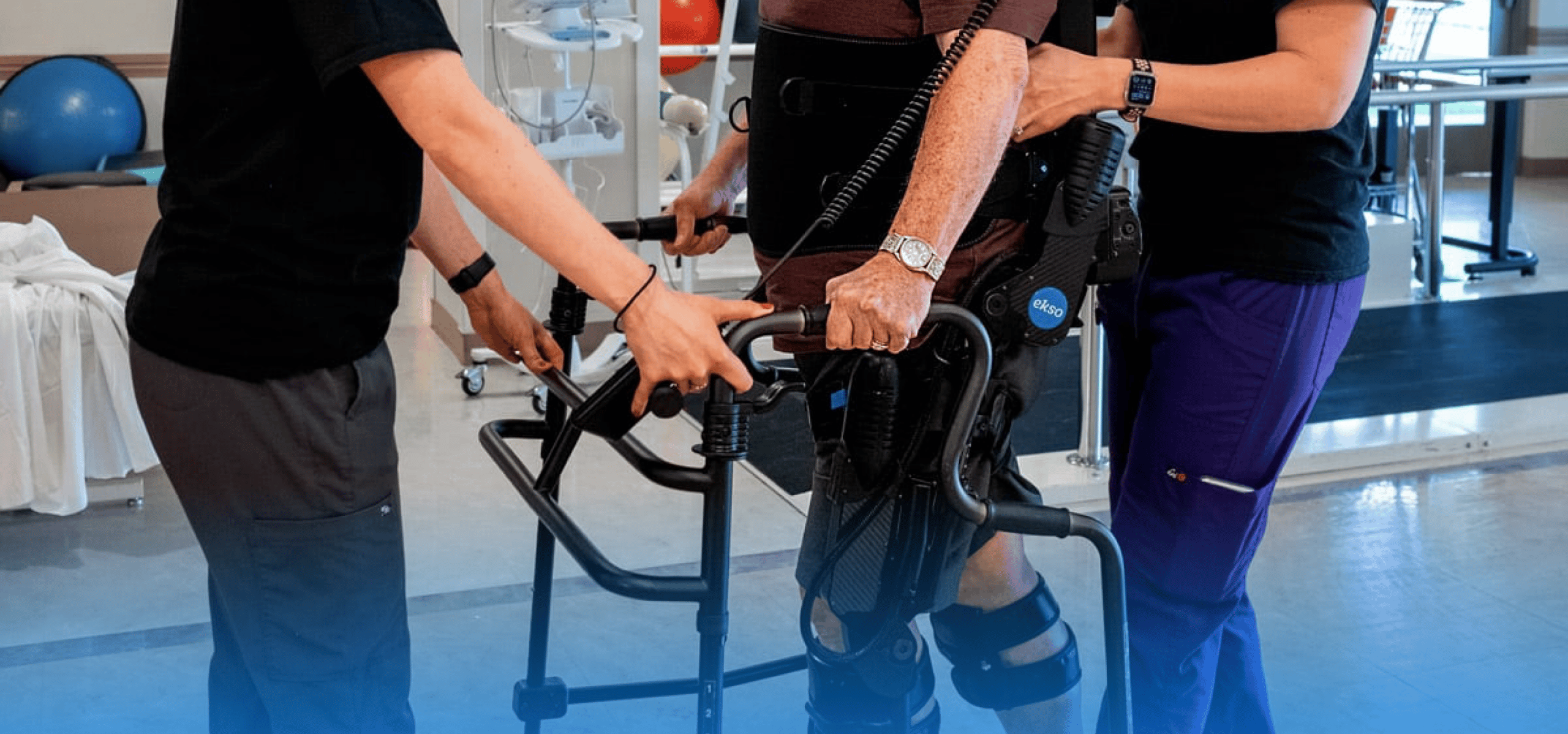
Robotic legs are powered medical exoskeletons that are fastened to the lower back and legs. They usually have motors and sensors attached to the hip and knee joints which coordinate and adjust with each step. Some robotic legs are customized to the wearer’s needs, allowing them to perform various tasks, including driving. To break it down further, a medical exoskeleton is any robotic system that patients with conditions like stroke, multiple sclerosis, brain injuries, and spinal cord injuries can wear to support movement.
Exoskeletons represent the coming together of man, machine, and work by responding to the user’s movement. They provide motor support to the wearer through patient-initiated movement or based on the setting the physical therapist uses and dependent on the patient’s needs.
Operating an exoskeleton is pretty easy for both you and your patient. The wearer only needs to shift their weight in the direction they want to move. The sensors then pick up the intended movement and offer support. With a powered exoskeleton, the wearer can stand from a sitting position, walk, and may even climb stairs. However, it is essential to note that these activities require training.
Robotic wearable technology has a wide range of applications and can be used by people with spinal cord injuries, brain injuries, multiple sclerosis, and stroke. According to Conor Walsh, a roboticist at Harvard University, “Robotic technology has recently expanded to benefit stroke patients. More than 70% of people who suffer a stroke never regain their full walking capacity.” At the same time, exoskeletons are not limited to medical uses only. They are also used by industrial workers like construction workers and warehouse workers to support the lifting of heavy loads. In fact, some companies have made it mandatory for workers to use exoskeletons as part of their personal protective equipment. They include: Ford, BMW, Hyundai, Samsung, and Mitsubishi, among others.
Paraplegic Conditions That Are Supported by Exoskeletons

One of the conditions we highlighted that is a common cause of paraplegia is spinal cord injury. When spinal cord injuries happen, they interfere with the communication between the brain and body parts below the injury, leading to paralysis. Exoskeletons can be used to support paralysis caused by spinal cord injuries, including injuries to the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions.[5]
To support this assertion, several studies have been conducted to investigate and verify the usefulness of exoskeletons for paraplegic conditions. In a 2018 study concerned with the development and control of a robotic lower limb exoskeleton for patients with paraplegic conditions, healthy subjects tested exoskeletons by performing normal daily activities like walking, standing, and sitting. It was concluded that the exoskeletons had natural gait cycles which support ambulation. [6] In simple terms, it demonstrated the exoskeleton’s ability to aid the rhythmic movement of a stride, which is needed in walking.
Exoskeletons have been shown to have a high impact on people with disabilities who were trying to regain muscle activity in their thighs, hips, and legs. In a clinical trial published in Frontiers in Robotics and AI, it is reported that 62% – 72% of wearers who practiced using exoskeletons in physical therapy could achieve their walking goals within 12 sessions. It also noted that after the 36th session, 80%-84% of the study groups achieved their walking goals. [7]
To demonstrate how useful and practical exoskeletons are in patients’ recovery and daily activities, here are two stories of patients who rely on exoskeletons.
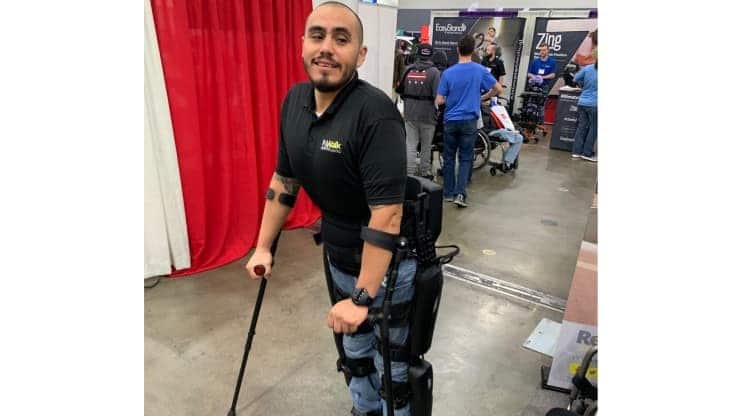
At 22 years old, Julio Caro, a structural steelworker in southern California, took an 18ft fall while working, which would change his life forever. He broke his back in two different places, injured his spine, and was unable to walk after the ordeal.
“I was young, and so I didn’t understand what was happening,” Caro said. “They said, ‘You’re not going to be able to walk again,’ and I thought they were lying.”
“I just wanted to get back on my feet — I was out to prove everybody wrong,” he added. “So when I first heard [about exosuits], I was, like, Robocop. As soon as I saw the machine and I saw it walk, I thought, ‘Oh cool, it does everything for you.’”
After using the exoskeleton for only five sessions in physical therapy, Caro was able to walk again. He says it made a lot of difference having the robotic legs as they allow him to work again and enjoy what we might typically take for granted, like reaching out and touching a leaf.
“I’m glad this technology is out there, [and] it’s only getting better,” he added.
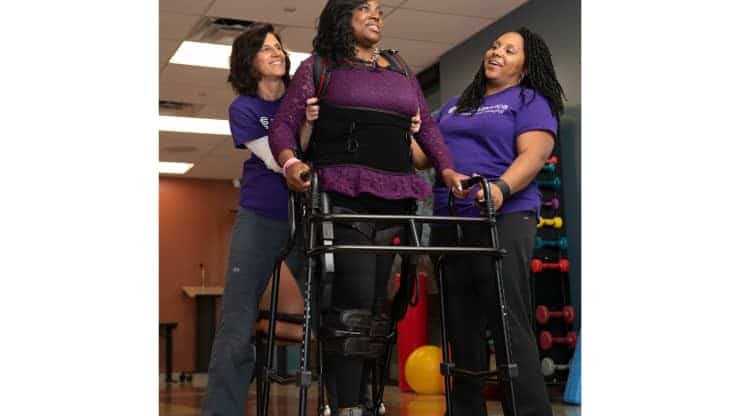

On Tuesday, December 4th, 2018, Amelia Clark dropped off her three sons at school and went to a hair-coloring class. She had a headache but thought nothing of it. She dismissed it as low blood sugar until the unthinkable happened. She couldn’t stand up.
“I must have passed out because when I woke up, I saw a whole bunch of lights, and the doctor said, ‘Hi. What’s your name? You’ve had a stroke.’”
Clark was hospitalized for a month and a half, unable to walk without any assistance. The first time she took a step after her stroke was when she was introduced to an exoskeleton, EksoNR. In just three months, she was able to walk with a cane and, by August, started driving again.
Benefits of Robotic Legs

- Robotic Legs Don’t Require Surgery
One great thing about robotic legs for physical therapy patients is that, unlike other treatments, they don’t require invasive surgical procedures. For instance, in epidural stimulation, a device is implanted near the spine, and in stem cell transplants, spinal cord injections are done. Conversely, robotic legs (exoskeletons) are worn on the body, making them an easy way to improve mobility without risk of complications.
- Robotic Legs Improve Circulation
When you have a spinal cord injury, blood tends to pool in the legs due to lack of movement, reducing the amount of blood flowing to the heart. It can also lead to swelling in the legs. Using exoskeletons can allow your patients to ambulate and move paralyzed areas. This contributes to the circulation of blood which is essential in supporting cellular activity.
- Robotic Legs Reduce Muscle Atrophy
Movement is very critical as it helps in strengthening muscles and bones. However, patients with paraplegic conditions may not be able to move around much. This can cause their muscles to reduce in size to conserve energy, hence the need for robotic legs. Though they do not stop muscle atrophy, they help maintain bone and muscle density as they keep the wearer moving and bearing their own weight.
- Robotic Legs Boost Confidence
When a patient experiences an injury or condition that affects their lower limbs, the recovery outlook is painted as marginally lower, and this can impact patient confidence. One of the most invaluable benefits of robotic legs is the hope they restore to patients who’ve been told they’ll never be able to walk again. Robotic legs represent an opportunity for them to walk again, which not only helps them become more independent but also more confident. Robotic legs can be used for rehabilitative exercises and help patients with complete SCI regain more mobility than they thought possible.
- Robotic Legs Help Manage Spasticity
One of the most common problems that patients with paraplegia face is a painful condition known as spasticity (the contraction of muscles). Robotic legs can help manage spasticity and improve other related conditions like pain and bowel function. When one robotic leg user was asked, she said that tending to her bowels took roughly 20 minutes, which was different from the hour she usually spent without an exoskeleton. [8]
The Best Robotic Legs for Paraplegic Conditions

There are different types of exoskeletons available in the market for paraplegic conditions that assist physical therapists, additionally, these exoskeletons have been approved for use in communities and medical institutions with supervision. One great example is Ekso Bionics’ EksoNR which is used to rehabilitate people after spinal cord injury, stroke, brain injury, and MS.
The EksoNR is like a backpack that extends to the legs and supports the torso and lower limbs. It has sensors on the footplates which signal the movements of the wearer. The exoskeleton then creates feedback and offers support to the wearer, depending on the settings. It not only supports ambulation but also helps patients regain muscle activity.
Where Can You Get Robotic Legs?

Robotic legs like the EksoNR and EksoGT are readily available in more than four hundred rehabilitation centers globally. If you’d like to acquire exoskeletons for your facility, you can contact our sales team by clicking here.
Conclusion

Robotic legs are essential for patients with paraplegic conditions. They help support movement, reduce muscle atrophy, and address other related conditions like pain, bowel function, spasticity, and overall quality of life.
Ekso Bionics has been at the forefront of creating the best quality medical exoskeletons for over a decade. Our EksoNR was one of the first FDA-approved medical exoskeletons for rehabilitation, and it continues to be the exoskeleton of choice for rehabilitation clinics. Please review our indications for use to determine eligibility. [9]
References:
- https://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/pubs/tbi_report_to_congress.html#:~:text=Traumatic%20brain%20injury%20(TBI)%20is,people%20are%20hospitalized%20and%20survive.
- Paralysis statistics – Reeve Foundation https://www.christopherreeve.org/living-with-paralysis/stats-about-paralysis
- Robotic Rehabilitation and Spinal Cord Injury: a Narrative Review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6095795/
- Exoskeleton Market Size & Share Report, 2022-2030 https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/exoskeleton-market
- Robotic Rehabilitation and Spinal Cord Injury: a Narrative Review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6095795/
- Development and control of a robotic lower limb exoskeleton for paraplegic patients https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0954406218761484?journalCode=picb
- How Exoskeletons Can Help People With Paraplegia Walk Again https://backend.eksobionics.com/how-exoskeletons-can-help-people-with-paraplegia-walk-again/
- Robotics are helping paralyzed people walk again, but the price tag is huge – The Washington Post https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2017/06/10/robotics-are-helping-paralyzed-people-walk-again-but-the-price-tag-is-huge/
- Indications for Use – Ekso Bionics https://backend.eksobionics.com/indications-for-use/