Postoperative therapy is a big part of the recovery process and is necessary to restore joint movement, strength, and flexibility. It might be required after surgical procedures like orthopedic, cardiac, thoracic, neurological, and abdominal surgery. Many patients may prefer skipping this step of their recovery, but this can result in improper or incomplete healing.
Postsurgical therapy is helpful if you are experiencing stiffness, pain, muscle weakness, reduced mobility, reduced balance, and reduced coordination. It also helps with any physical and psychological effects you may have endured due to surgery.
According to a National Institutes of Health (NIH) study, patients who stay in bed after surgery tend to lose muscle strength, heart capacity, and lung capacity due to a lack of physical activity. [1] But with the incorporation of physical therapy in recovery, you can prevent functional atrophy. This article will explore the phases of postoperative rehabilitation, types of physical therapy, and the benefits of postoperative rehabilitation.
The 3 Phases of Postoperative Rehabilitation

There are three main phases in postsurgical rehabilitation, and they differ from patient to patient depending on the type of surgery. They are broken down into:
- Stage 1: In this stage, you’ll be immobilized as you’ll be fresh from the surgery room. Typically, you’ll be in pain, and the surgical area will be swollen. At this point, rest is recommended for a few hours or days, depending on the type of surgery.
- Stage 2: In this stage, the pain and swelling will reduce. You’ll be able to move a little and will be ready to start physical therapy. The goal, at this point, is to strengthen the body, improve stability, and restore range of motion.
- Stage 3: In this stage, you’ll be continuing to heal and are ready to rehabilitate and learn to complete your activities of daily living. The ultimate goal of physical therapy will be achieved in this stage.
Surgery Operations That Require Postoperative Physical Therapy

These are five surgical procedures that necessitate physical therapy as part of the recovery process. They include:
- Brain tumor surgery: A 2019 pilot study on the effectiveness of rehabilitation therapy after brain tumor surgery reported that intensive rehabilitation resulted in improved motor function, cognition function, and Activities of Daily Living (ADL). [2] In this case, physical therapists focus on range-of-motion exercises, balance, gait, and endurance training.
- ACL and Meniscus Repair: ACL knee ligament and meniscus cartilage repair is a problem often associated with athletes. According to a 2019 study conducted by the International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, physical therapy is vital in hastening the healing process and avoiding re-injury. Physical therapists usually focus on building quadriceps and hamstring strength in the recovery process. [3]
- Back and Spine Surgery: Physical therapy is vital, especially because of the delicate nature of spinal surgeries. Your physical therapist will show you exercises and movements for your back that don’t put pressure on your spine. Therapy strategies normally include stretches and exercises that get the blood flowing. In the case of more invasive surgeries, for example, spinal fusion, your therapist can monitor your back health and update your doctor on the healing progress.
- Heart Attack/Bypass Surgery: According to a 2018 study by the Journal of Physical Therapy Science, preoperative physical therapy can help prevent cardiopulmonary complications by offering patients a safe space to move. Low-impact exercises tend to improve health and reduce your stay in the hospital. Coupled with postoperative therapy, you can recover faster while avoiding all postsurgical complications. [4]
- Achilles Tendon Release (Tenotomy): This is a type of surgery that is done to fix a damaged or contracted Achilles tendon. This procedure can be performed to relieve shortened and stiff muscles to allow for better range of movement. This is a common problem for patients with spinal cord injuries because, after a spinal cord injury, the normal flow of nerve signals is disrupted and feet tend to relax into a toe-pointed position. This could limit a person’s ability to stand if not corrected.
Major Types of Physical Therapy For Postoperative Patients
Physical therapy strategies are not one-size-fits-all. The type of therapy recommended always depends on your physical condition and biomechanical needs. In this section, we will explore rehabilitation methods that are applicable to patients who have undergone any kind of surgery.
- Stretching
After surgery, the soft tissue normally contracts, and scar tissue forms. This can decrease flexibility and make it difficult for you to move. However, regular stretching can help prevent immobility caused by scar tissue. It also helps increase joint flexibility and a full range of motion in case of joint surgeries. Overall, stretching makes life much easier and allows you to do simple tasks like reaching over your head, walking, and even climbing stairs.
Stretching has also been shown to help improve balance and reduce pain by relaxing tense or spasming muscles. Lower back, abdominal, hip, and leg muscle stretches are recommended if you’ve undergone back surgeries.
Common hamstring exercises targeting the outer hip and lower back include Knee to Chest Stretch, Figure 4 Stretch, Pigeon Stretch, and Doorway Hamstring Stretch. These stretches are particularly great for tight and restricted muscles. The Pigeon Stretch and Doorway Hamstring Stretch are more advanced and should only be performed in a pain-free range. Other types of stretches used in postoperative therapy include:
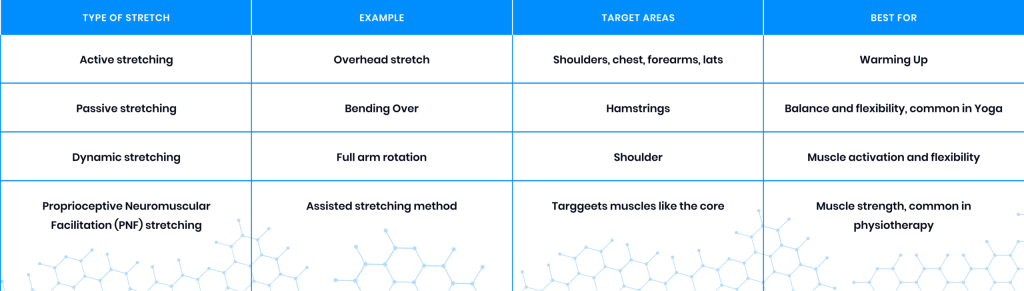
- Range of Motion Therapy
Range of motion (ROM) is concerned with how far you can move an affected joint or limb in all directions and positions naturally without strain and pain. There isn’t one standard definition of ROM. According to Dr. Aldalbert Kapandji, who specializes in physical therapy, range of motion is “the extent of osteokinematic motion available for movement activities, functional or otherwise, with or without assistance.” [5]
Range of motion exercises increase movement, reduce pain, and improve joint integrity and function. Range of motion exercise and stretching are generally performed in the first phase of rehabilitation to help regain joint functionality before moving to more advanced practices.
Range of motion therapy normally includes:
- Passive routines where the therapist guides your movements.
- Interactive routines where both you and the therapist do the work.
- Active routines where you do the exercises on your own.
Range of motion exercises involving circling joints and knee extensions are beneficial in different situations, including:
- Soft tissue and joint recovery
- Joint and soft tissue mobility
- Neuromuscular reeducation
- Synovial movement enhancement
- Strengthening
Strengthening exercises are a crucial part of physical therapy and help improve muscle function around the surgical area. Strengthening exercises are customarily performed alongside or after the range of motion exercises because increased joint movement without an equal increase in strength might cause injury.
Strengthening exercises are also vital in improving your core strength. The core is a major focus area because it is the source of stability. Rebuilding core strength improves stability and mobility and helps prevent additional injuries. It allows you to increase the load you can handle without overexerting and injuring yourself. In addition, strengthening can also be used for the back and pelvis areas. Strengthening exercises typically include leg raises, hamstring and quadriceps contractions, and squats using a chair.
Strengthening exercises can also include bridge exercises and ball bridge exercises. These exercises are great for strengthening the hamstring, lumbar extensor, pelvic, back, and buttocks. These exercises should be done in a pain-free range; once you’ve mastered them, you can move on to more advanced strengthening exercises.
- Ultrasound and Electrical Therapy
Ultrasound and electrical therapy help improve blood flow and retrain nerves. Ultrasound therapy involves the use of high-frequency sound waves on deep tissue. The high-frequency sound waves used to stimulate deep tissue are so low that even the human ear cannot pick them up. This type of therapy utilizes a probe for administration and is known to reduce pain, accelerate healing, and reduce inflammation in the soft tissues. A 2014 study conducted by the Journal of Physical Therapy Science reported that therapeutic ultrasound increases range of motion and pain threshold for at least 20 minutes. [6]
Electrical therapy involves the use of low electrical current on the deep tissues. Electrical stimulation works by sending small electrical currents to the targeted area and the nerves surrounding it. It is extremely helpful in increasing blood flow, pain management, and improving muscle flexibility. A 2021 study conducted by Frontiers in Medicine reported, “As a supplementary treatment after total knee arthroplasty, postoperative neuromuscular electrical stimulation could improve the short-term to long-term quadriceps muscle strength, mid-term pain, and mid-term function.” [7]
- Gait Training
Walking is a great physiotherapy technique that’s primarily used for neurosurgery patients. It normally involves rewiring and training the brain to control walking muscles. This is achieved because of the brain’s neuroplasticity – the ability of the brain to form and reorganize synaptic connections. When walking is practiced regularly after surgery, it allows the brain to strengthen and create neural pathways that support movements involved in walking. Some high repetition walking exercises include leg and balance exercises.
Benefits of Postoperative Therapy

General Surgery
A postoperative therapy program after general surgery is a crucial part of recovery and offers a host of benefits like:
- Proper Healing and Faster Recovery Time
Many complications can arise after surgery, including infection and muscle atrophy, which might lead to poor healing. That’s why postoperative therapy is important. Postoperative therapy can help wounds heal properly by minimizing scar tissue, retraining muscles, and recovering joint function. It also allows you to enjoy a faster recovery time. According to a 2017 study conducted by Acta Medica, beginning physical therapy following a joint replacement surgery can reduce your hospital stay and help you recover faster. [8]
- Patient Participation
Patients who actively participate in their own recovery process have been shown to have better results and recovery experiences than those who don’t in a 2013 review conducted by researchers from the Health Policy Research Group at the University of Oregon. [9]
- Improves Mobility
Joint replacement surgeries normally result in reduced mobility, making activities that may seem ordinary, like walking, difficult. This happens because of the body’s natural response, which is to protect the area of surgery by swelling, reducing the range of motion, and tightening the muscles. This makes physical therapy extremely important, especially after knee and hip replacement surgeries, as it may help you recover your mobility through targeted postoperative therapy practices.
- Eases Pain and Swelling
Swelling and pain after surgery normally vary from one person to another. The pain usually arises when chemicals that stimulate nerve endings are released, and the excess inflammation compresses the nerves. Exercises are a great tool for reducing swelling, which results in improved mobility, faster healing, and reduced pain. Postoperative physical therapy administration can also help in preventing chronic pain.
According to a 2013 review conducted by London-based medical researchers, postoperative therapy is quite effective in improving short-term lower back pain and long-term lower back and leg pain if you’ve undergone lumbar spinal stenosis surgery. [10]
- Reduces Scar Tissue Formation
During the healing process, scar tissue forms, and tissues contract. This normally leads to scarring and reduced mobility. However, mobilization techniques can help prevent this using ultrasound therapy, which effectively increases flexibility and softens the scar tissue. According to a 2016 study conducted by researchers for the Internal Medicine Review journal of Washington D.C., low-intensity therapeutic ultrasound can help treat soft tissue injuries and improve musculoskeletal and post-operative recovery outcomes. [11]
- Reduces the Development of Secondary Issues
Physical therapy can help reduce surgical complications like blood clots, and infection, among others. Specific exercises and movements may help in reducing the risk of contractures and other complications.
- Improves Flexibility
Staying in bed after surgery is detrimental for you, and it may lead to weak muscles, which will make you susceptible to injury. When your joints become stiff, activities like walking, climbing stairs, and reaching overhead can be compromised. However, stretching exercises can help you keep your joints flexible and muscles limber.
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery is involved with the treatment of conditions affecting the nervous system, including the spinal cord, brain, and peripheral nervous system. This makes postoperative rehabilitation very important as part of helping a patient regain their pre-surgery functionalities. Benefits attributed to physical therapy include:
- Increased Range of Movement – Patients are able to increase their limb and joint movement in any direction without any pain.
- Improved Gait – Physical therapy can help you improve your balance, coordination, and walking movement control.
- Increased Muscle Strength – Physical therapy is great for training leg and back muscles to support the weight of the body.
- Reduced Spasticity and Contractures (Shortened Muscles) – Surgery may lead to muscle tightness, otherwise referred to as spasticity, which can limit movement and cause pain. But physical therapy can help you avoid these complications.
Conclusion

Postoperative therapy is vital when you are recovering from surgery, and its efficacy has been shown in different studies. It will help you heal faster, regain mobility, reduce pain, and prevent postoperative complications. In case you’ve undergone surgery, physical therapy will offer you the recovery support you need on your healing journey.
References:
- Assessing the effectiveness of routine use of post-operative in-patient physical therapy services https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5506300/
- Intensive Rehabilitation Therapy Following Brain Tumor Surgery: A Pilot Study of Effectiveness and Long-Term Satisfaction https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6509576/
- Restoring knee extensor strength after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a clinical commentary https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6350662/
- Prevention of postoperative pulmonary complications through preoperative physiotherapy interventions in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft: literature review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6110234/
- The clinical evaluation of the upper limb joints’ function: back to Hippocrates https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0749071203000295?via%3Dihub
- Effects of Therapeutic Ultrasound on Range of Motion and Stretch Pain https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4047237/
- Effect of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8677678/
- Early rehabilitation after elective total knee arthroplasty https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6357664/
- What the evidence shows about patient activation: better health outcomes and care experiences; fewer data on costs https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23381511
- Rehabilitation following surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis – McGregor, AH – 2013 | Cochrane Library https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD009644.pub2/abstract
- Low-Intensity Ultrasound for Promoting Soft Tissue Healing: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Medical Technology https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6128661/
